Sure! Here’s a rewritten version of the article in English with titles formatted as you requested:
Google DeepMind is Google’s division focused on artificial intelligence. It develops deep learning algorithms that enable AI agents to learn autonomously without prior programming. Discover the history of Google DeepMind, how it operates, and how Google utilizes it to enhance its various products and services.
What is Google DeepMind?

Google DeepMind is a division of Google dedicated to artificial intelligence. It emerged after Google acquired DeepMind in January 2014 for £400 million. Previously, the startup collaborated with University College London. DeepMind employs about 140 researchers at its facilities in Kings Cross, London.
Moreover, Google DeepMind’s Vice President of Engineering is Demis Hassabis, the co-founder of the company. This neuroscientist was also a video game designer in his youth, working with Peter Molyneux on titles like Syndicate and Theme Park. He also founded Elixir Studios, the development studio behind the game Evil Genius, where players take on the role of a villainous mastermind.
Objective of DeepMind
DeepMind aims to create intelligent machines that are capable of learning and acquiring new knowledge in a way similar to humans. To achieve this, DeepMind develops powerful general learning algorithms that can be combined to create AI systems, also known as AI agents. These systems learn automatically without being pre-programmed, and human intervention in their learning process is minimal.
Additionally, the company seeks to provide its algorithms with a vast array of raw information, allowing them to learn and utilize this knowledge to act, classify, or predict. Being general systems, they logically perform many tasks.
Thus, the company initially let its algorithms learn to play Atari video games, subsequently using the acquired knowledge to solve problems across various specific domains. This is a radically different approach from that adopted in the early days of artificial intelligence, where AI tools were typically pre-programmed to solve specific tasks. Mustafa Suleyman argues that the systems developed this way are rigid, static, and unable to manage novelty or adapt to new parameters. Consequently, they are fundamentally limited.
A Specialist in Reinforcement Learning Techniques
AGI (artificial general intelligence) refers to flexible, adaptable systems and tools capable of learning. To develop its systems, DeepMind employs a reinforcement learning architecture. It all begins with an agent, which is assigned a goal or set of rules for interacting with an environment.
This environment can be a physical domain, a commercial environment, a robotic environment, or even an Atari game. The agent acts within the environment and receives feedback in the form of observations, which facilitate updates to its behavior rules.
How Google DeepMind Works
The technology utilized by Google DeepMind is quite complex. To simplify, hierarchical networks have existed since the 1980s, and were reused by experts in Toronto and New York. The fundamental idea is to take raw pixel data or data from sensors that need to be classified or recognized.
This allows for the identification of structure within vast datasets. Thus, certain conditions can be imposed on the network to produce recognizable and usable labels or classifications for humans.
Testing Google DeepMind

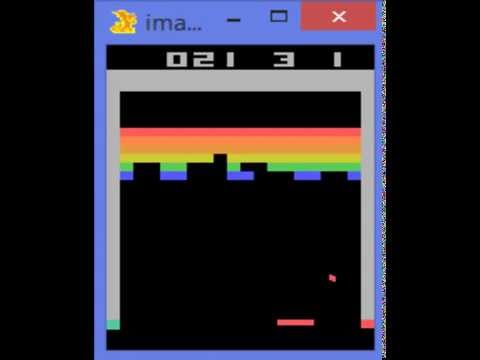
To test the capabilities of its artificial intelligence, Google DeepMind utilizes the Atari arcade game platform, dating back to the 1970s. Agents play games like Space Invaders, learning to master them over successive rounds. This process also allows agents to train and acquire general skills.
With each image, the agent receives raw pixel data and score information, representing about 30,000 inputs per image. The agent is connected to the control buttons but does not receive instructions regarding the effects of each button. It must discover for itself the effects produced by these real-world tools and how to use them. The agents aim to achieve the highest possible score.
Google DeepMind and Video Games
At each input of information, the agent tries to discover the optimal action based on that information. It repeats this process over time in an attempt to optimize its score. When playing Space Invaders for the first time, an agent struggles to hide behind the orange obstacles and tends to shoot randomly. It gets killed repeatedly and has no idea what to do in this virtual environment. Later, once trained, the agent learns to control its avatar, hitting the target with every shot.
It manages to find the enemies that yield the most points and rarely gets hit. Ultimately, the agent completes the game without making any mistakes and performs better than a human player. In 57 games, the AI agent outperformed a human in 49 of them. This is how DeepMind managed to defeat the South Korean Go champion, considered the best player in the world, Lee Sedol, with its Google DeepMind AlphaGo agent in 2016.
Google DeepMind and Board Games
Google DeepMind Chess is the version of AlphaGo dedicated to learning chess. The renowned strategy board game in its digital form is well within the capabilities of DeepMind’s deep learning program. Stockfish 8, regarded as the most advanced chess program, was defeated by Google DeepMind AlphaGo in December 2017. The four-hour confrontation, spanning 100 games, resulted in an impressive score for the AI.
It achieved 28 wins, 72 draws, and 0 losses. It took only nine hours for it to learn the rules of the game and master it comprehensively. The research team is likely to organize a match against a human champion, similar to IBM’s Deep Blue, which defeated champion Garry Kasparov in 1997.
Since then, AI algorithms have been training on the real-time strategy video game Starcraft II. It is not yet capable of competing with a human player. It must learn 300 basic actions, working with the much larger spatial limits than the Go and Atari games. However, the open APIs for developers of Starcraft II from Blizzard, the game’s publisher, will improve their AI’s performance, a crucial aspect in such video games.
How Google Uses DeepMind

Google employs DeepMind’s algorithms to make some of its most popular products and services smarter. In 2012, thanks to DeepMind, Google’s image recognition reduced its error rate to 16%, and then to 5.5%. This error rate is comparable to that of a human. This technology is utilized in Google’s image search functionality.
Deep learning is also used for text recognition and translation, as well as for local search and voice recognition. In this area, in 2012, DeepMind contributed to a 30% reduction in error rates, the largest improvement in 20 years.
Google DeepMind’s artificial intelligence is also employed for fraud detection, spam detection, and handwriting recognition. Over 60 rule-based systems have been replaced by deep learning-based networks. Recently, Google’s AI has even been able to create artworks. It’s clear why Google was interested in DeepMind, prompting them to invest a significant sum to acquire this startup.
Should We Fear Google DeepMind?

Many scientists fear that artificial intelligence could turn against humanity and lead to its destruction. Despite these warnings, Google appears determined to utilize artificial intelligence. It does not seem concerned about potential future ramifications. According to DeepMind, if such a risk does exist, it tends to distract from the real ethical and security questions that need to be addressed regarding artificial intelligence.
Like all tools in this world, the power of artificial intelligence can potentially be misused. However, it is possible to control tools like a washing machine or a tractor. It is likely, however, that humanity may lose control of AI in the future. Just like the development of nuclear weaponry or chemical weapons production, caution and gradual advancements in this field are necessary.
Fully aware of the impacts of deep learning algorithms, this subsidiary of Alphabet began research on ethics in October 2017. It currently has a unit composed of eight researchers, with plans for this number to increase to 25 by early 2018. This unit aims to assess the impacts of AI research on privacy, the emergence of autonomous weapons, automation, transparency, and more. It’s important to note that a subsequent paragraph had put Google DeepMind’s communication in jeopardy.
Google DeepMind: Illegal Use of Health Data in the UK
The ICO investigation into the partnership between Google DeepMind and three London hospitals has resulted in a ruling of non-compliance with privacy data protection law.
Our colleagues at objetconnecte.com reported the issue. The agreement between Google DeepMind and the three London hospitals sparked significant backlash. Many of the 1.6 million patients whose medical data was shared with the tech giant expressed their discontent.
The goal was to improve Google DeepMind’s algorithms using this critical information. Ultimately, it aimed to enhance cutting-edge medical solutions. However, the partnership between the Royal Free NHS Trust, the manager of the three hospitals, and Alphabet’s AI subsidiary raised concerns about the consent of users, who should have been able to retroactively opt-out of their medical data being utilized.
The Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO), the UK equivalent of CNIL, subsequently took up the case. Its conclusions favored the patients. Moreover, it highlighted the lack of transparency from the manager and Google.
According to the ICO’s notes, patients were not adequately informed about the use of their data. Until now, it was difficult to know whether a particular medical record was used to develop the test version of the Streams application, a predictive analytics tool for sepsis.
Necessary Legal Compliance
For greater clarity for the British authority and the patients, the two entities must comply with privacy data protection law. They must also disclose the type of information being used. While Royal Free NHS and DeepMind defend themselves by emphasizing their intention to save lives, the ICO insists on not compromising on privacy principles during testing.
Both parties will need to conduct a privacy impact assessment during the testing phase to ensure the protection of records going forward. This conciliatory response from a country exiting the European Union is considerably different from the punitive considerations of the GDPR, the General Data Protection Regulation.
Google DeepMind and Royal Free NHS have already expressed their willingness to adhere to these guidelines. They also wish to report on the progress of the Streams application while boasting improvements in their personal data management policies.
DeepMind AlphaFold 2 Revolutionizes Drug Development
In December 2020, DeepMind won the “Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction” (CASP) algorithm competition. The participants in this competition aimed to determine the 3D shape of a protein based on its DNA sequence.
The AI that enabled DeepMind to overcome this challenge is called AlphaFold 2. This system was trained for a few days using 128 TPUs. This is significantly less than what was required to train AlphaGo.
However, this training was sufficient for the AI to learn to predict a protein’s structure. Its performance, speed, and accuracy significantly surpassed other algorithms presented during the CASP competition.
The system also outperforms existing methods, such as X-ray crystallography. Indeed, AlphaFold is cheaper and much faster.
Thanks to this achievement, DeepMind has addressed a 50-year-old scientific challenge. Researchers can now use AI to identify the structure of all the proteins in the human body and potentially use these proteins as targets for molecules to develop new drugs.
So far, only a quarter of the human proteome has been targeted for drug molecules. Evidence of its practical utility: AlphaFold 2 has already been used to predict the structure of the ORF3 protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes COVID-19. This represents another triumph for DeepMind and a significant advancement in the healthcare field.
The Universal AI Assistant and Its Deep Think Capabilities
The Gemini model (in its Flash, Pro, and Ultra versions) has become the flagship offering of Google DeepMind. It embodies the ambition to create a universal AI assistant capable of reasoning, planning, and acting across various digital environments.
The 2.5 Pro model has been enhanced with an experimental Deep Think mode. It employs parallel reasoning techniques and reinforcement learning, echoing DeepMind’s initial methods. This mode enables Gemini to reflect on its thoughts before responding, enhancing its ability to solve complex problems, particularly in coding and scientific research.
The model achieved a symbolic victory, outperforming human teams during an international coding competition (ICPC 2025), an accomplishment compared to the impact of AlphaGo.
One of Gemini’s strengths is its increasing agency. It acts as an agent capable of using external tools (through tool use) and integrating natively into the Google ecosystem (Gmail, Drive, Docs, Search, and even Maps and Google TV).
The regular updates (known as Gemini Drops) in October 2025 have also enhanced its multimodal capabilities, offering a better understanding of imported images and diagrams. It has also enabled video generation with the Veo model.
Light versions such as Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite have been optimized to be more cost-effective and faster, while enhancing translation and audio transcription. Furthermore, the dedicated Gemini application is on track to gradually replace Google Assistant on Android and Pixel devices, establishing itself as the default conversational interface for interacting with smartphone functionalities.
These developments signify the transition of generative AI from the lab to becoming a daily and strategic assistance tool for Google.
FAQ
Google DeepMind is Google’s division dedicated to artificial intelligence, stemming from the acquisition of the DeepMind startup in 2014. Its primary objective is to create intelligent machines capable of learning and acquiring new knowledge in a manner similar to humans (Artificial General Intelligence – AGI), by developing general learning algorithms, especially through reinforcement learning.
Google DeepMind primarily uses the Reinforcement Learning approach. In this method, an agent interacts with an environment (like an Atari video game or Go), receives feedback in the form of observations, and adjusts its behavior rules to achieve a given goal (such as scoring the highest points).
DeepMind’s AI, notably AlphaGo (in 2016) and AlphaFold 2 (in 2020), has achieved several victories and made significant advancements. It defeated the world Go champion, outperformed the best chess programs (AlphaGo Zero), and, with AlphaFold 2, solved the scientific challenge of predicting protein structures, paving the way for new drug development.
Google utilizes DeepMind’s algorithms (Deep Learning) to make its products and services smarter. These applications include improving image recognition, translation, voice recognition (significantly reducing error rates), spam and fraud detection, and enhancing user experience with the universal AI agent Gemini.